Bicentennial Quarter Errors: Unveiling Rare Finds and Their True Value
The 1976 Bicentennial Quarter, commemorating the 200th anniversary of the Declaration of Independence, was a widely circulated coin. However, like any mass-produced item, errors occurred during the minting process. These “bicentennial quarter errors” have become sought-after collectibles, sometimes fetching significant sums. This comprehensive guide dives deep into these errors, providing insights into identification, valuation, and the factors that contribute to their desirability. We aim to provide the most comprehensive, expert-driven resource available, empowering you to identify potential treasures and understand their true worth. This isn’t just about spotting a mistake; it’s about understanding numismatic history and the art of collecting.
Understanding Bicentennial Quarter Errors: A Deep Dive
Bicentennial quarter errors encompass a wide range of anomalies that occurred during the minting process of the 1976 Washington quarter. These errors can range from minor imperfections to dramatic misprints, each affecting the coin’s value differently. Understanding the nuances of these errors requires a keen eye and a basic knowledge of the minting process. We’ll explore the most common types of errors, their causes, and how they are graded by numismatists.
What Constitutes a Bicentennial Quarter Error?
An error occurs when something goes wrong during the minting process, resulting in a coin that deviates from the intended design. This can include issues with the dies (the tools used to strike the coin), the planchets (the blank metal discs), or the striking process itself. Even slight variations can create a unique, and potentially valuable, error coin. Errors are distinct from damage that occurs after the coin leaves the mint, such as scratches or dents.
The Minting Process: Where Errors Can Occur
The minting process is complex, involving several stages where errors can arise:
* **Die Creation:** The dies, which contain the design of the coin, are created through a multi-step process. Errors can occur during the master die creation, hubbing, or working die creation.
* **Planchet Preparation:** Planchets must be correctly sized, shaped, and cleaned before striking. Problems in this stage can lead to errors such as clipped planchets or improper metal composition.
* **Striking:** The planchet is struck between the obverse (front) and reverse (back) dies under high pressure. Misalignments, double strikes, or insufficient pressure can result in errors.
* **Inspection and Packaging:** While quality control exists, some errors inevitably slip through. These are the coins that become sought after by collectors.
Why Bicentennial Quarter Errors are So Collectible
The Bicentennial Quarter was produced in massive quantities, but the allure of finding an error coin is powerful. The combination of historical significance and potential scarcity drives interest. Furthermore, the bicentennial design itself is iconic, making error coins visually striking. The discovery of an error coin can transform an ordinary quarter into a valuable piece of numismatic history. Recent trends in online coin collecting have further fueled the demand and increased awareness of these errors.
Identifying Common Bicentennial Quarter Errors
Several types of errors are commonly found on Bicentennial Quarters. Knowing what to look for is crucial for identifying potential valuable coins. We’ll cover the most frequently encountered errors and provide visual examples to aid in identification. Remember, proper identification is key to determining the coin’s worth.
Die Errors: The Most Common Type
Die errors occur when there are imperfections or alterations to the dies used to strike the coins. These errors are often replicated on multiple coins, making them more common than other types of errors.
* **Doubled Die:** This occurs when the die is struck more than once during its creation, resulting in a doubling of the design elements. Look closely at the lettering and date for signs of doubling. A true doubled die error will show doubling on multiple coins struck with that die.
* **Die Crack:** A die crack is a fracture in the die that appears as a raised line on the coin. These cracks can range from hairline fractures to prominent lines that cross the entire coin. The value of a coin with a die crack depends on the severity and location of the crack.
* **Die Chip:** A die chip is a small piece that breaks off the die, resulting in a small, raised blob on the coin. These are often found in the lettering or around the edges of the design.
* **Filled Die:** Debris can sometimes get lodged in the die, preventing certain details from being fully struck on the coin. This results in areas of the coin appearing weak or missing detail. For example, a filled die might cause the “D” in “United” to appear faint or incomplete.
Planchet Errors: Imperfections in the Blank Coin
Planchet errors occur when there are imperfections in the planchet before it is struck. These errors are less common than die errors but can be quite dramatic.
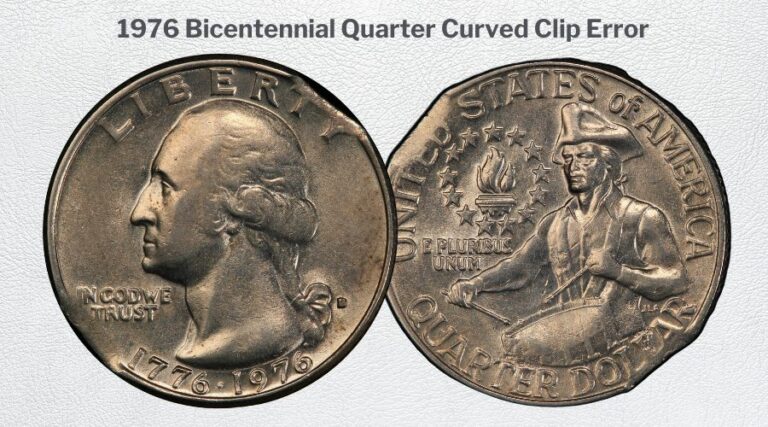
* **Clipped Planchet:** This occurs when a portion of the planchet is missing, resulting in a coin with a curved edge. Clipped planchets are created when the metal strip from which the planchets are punched is not fed properly, resulting in overlapping punches.
* **Lamination Error:** Lamination errors occur when the metal layers of the planchet separate, creating a peeling or flaking effect on the coin’s surface. These errors are caused by impurities in the metal.
* **Improper Metal Mix:** Occasionally, the composition of the planchet is incorrect, leading to discoloration or other unusual characteristics. These errors are rare and can be difficult to verify.
Striking Errors: Problems During the Strike
Striking errors occur during the actual striking of the coin, when the planchet is pressed between the dies.
* **Off-Center Strike:** This occurs when the planchet is not centered between the dies, resulting in a portion of the design being missing. The more off-center the strike, the more valuable the coin is likely to be.
* **Double Strike:** A double strike occurs when the coin is struck more than once, resulting in a doubling of the entire design or portions thereof. Double strikes can be dramatic and are highly sought after by collectors.
* **Broadstrike:** A broadstrike occurs when the retaining collar (which normally prevents the coin from spreading out too much) malfunctions, resulting in a coin that is wider and flatter than normal.
Numismatic Grading Services: The Key to Authenticity and Value
To ensure the authenticity and accurately assess the value of a bicentennial quarter error, it’s crucial to consider having it graded by a reputable numismatic grading service. These services provide expert authentication and grading, which is essential for serious collectors and investors.
Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS)
PCGS is one of the most respected and widely recognized coin grading services in the world. They offer a comprehensive grading service and encapsulate coins in tamper-evident holders, ensuring their authenticity and protection. PCGS-graded coins are highly valued in the numismatic market.
Numismatic Guaranty Corporation (NGC)
NGC is another leading coin grading service with a strong reputation for accuracy and integrity. Like PCGS, NGC provides authentication, grading, and encapsulation services. NGC-graded coins are also highly regarded by collectors and investors.
How Grading Affects Value
The grade assigned by a grading service significantly impacts the value of a coin. The Sheldon Scale, ranging from 1 (Poor) to 70 (Perfect Mint State), is used to assess the condition of the coin. A higher grade indicates better condition and, consequently, a higher value. Even minor differences in grade can result in substantial price differences, especially for rare or desirable error coins.
Valuation of Bicentennial Quarter Errors: Factors to Consider
Determining the value of a bicentennial quarter error involves considering several factors. These factors include the type of error, the severity of the error, the condition of the coin, and the current market demand.
Rarity and Scarcity
The rarity of an error is a primary factor in determining its value. Some errors are more common than others, while some are exceedingly rare. The rarer the error, the more valuable the coin is likely to be.
Condition and Grade
The condition of the coin, as assessed by a grading service, plays a significant role in its value. Coins in higher grades (e.g., Mint State) are generally worth more than coins in lower grades (e.g., circulated condition).
Market Demand
The current market demand for a particular error coin can fluctuate based on trends and collector interest. Factors such as media coverage, online auctions, and collector communities can influence demand.
Documentation and Provenance
Coins with documented history or provenance (e.g., coins from famous collections) may command a premium. Documentation can add to the coin’s appeal and increase its value.
Expert Coin Appraisal: Ensuring Accurate Valuation
For accurate valuation, consulting with a professional coin appraiser is highly recommended. A qualified appraiser can assess the coin’s authenticity, condition, and rarity, providing an informed estimate of its value. Finding a reputable appraiser is crucial for making informed decisions about buying, selling, or insuring your coins. The American Numismatic Association (ANA) offers resources for finding qualified appraisers.
Understanding the Appraisal Process
The appraisal process typically involves a thorough examination of the coin, including its physical characteristics, error type, and condition. The appraiser will also research recent sales data and market trends to determine the fair market value of the coin. A written appraisal will provide a detailed description of the coin and its estimated value.
The Future of Bicentennial Quarter Error Collecting
The interest in bicentennial quarter errors is likely to continue as more collectors discover the nuances and potential value of these coins. The accessibility of information and online marketplaces has made it easier than ever for collectors to buy, sell, and learn about error coins. As awareness grows, the demand for rare and well-preserved bicentennial quarter errors is expected to increase.
Technological Advancements in Coin Identification
Technological advancements, such as high-resolution imaging and artificial intelligence, are making it easier to identify and authenticate error coins. These tools can help collectors spot subtle errors that might otherwise be missed, improving the accuracy and efficiency of coin collecting.
Numismatic Product/Service: PCGS Coin Grading
Professional Coin Grading Service (PCGS) stands as a leading authority in the world of numismatics, offering unparalleled expertise in coin authentication, grading, and encapsulation. PCGS’s core function is to evaluate the condition and authenticity of coins, assigning them a grade based on the Sheldon Scale, a universally recognized standard in the numismatic community. This grading process is crucial for collectors and investors alike, as it provides a standardized measure of a coin’s quality and value.
Detailed Features Analysis of PCGS Coin Grading
PCGS offers a range of features designed to provide collectors and investors with confidence in their coin acquisitions. Here’s a breakdown of key features:
* **Authentication:** PCGS employs expert numismatists who meticulously examine coins to verify their authenticity, protecting collectors from counterfeit or altered coins. This ensures that any coin graded by PCGS is genuine and accurately represented.
* **Grading:** PCGS assigns a grade to each coin based on its condition, using the Sheldon Scale, ranging from 1 (Poor) to 70 (Perfect Mint State). This grade reflects the coin’s wear, surface preservation, and overall eye appeal, providing a clear indication of its quality.
* **Encapsulation:** Once graded, coins are sealed in tamper-evident, inert plastic holders. This protects the coin from environmental damage, handling, and further wear, preserving its condition and value.
* **Guarantee:** PCGS guarantees the accuracy of its grading. If a coin is later determined to be overgraded, PCGS will compensate the owner for the difference in value. This guarantee provides added assurance to collectors and investors.
* **Population Reports:** PCGS maintains detailed population reports that track the number of coins graded for each date, mint mark, and grade. This data provides valuable insights into the rarity and scarcity of specific coins.
* **Online Verification:** PCGS offers an online verification service that allows anyone to verify the authenticity and grade of a PCGS-graded coin using its certification number. This transparency helps build trust and confidence in the grading process.
* **Secure Storage:** PCGS offers secure storage facilities for certified coins, providing a safe and insured environment for valuable collections. This service is particularly useful for collectors with large or high-value collections.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of PCGS
The advantages of using PCGS for coin grading are numerous and directly translate to tangible benefits for collectors and investors.
* **Increased Value:** PCGS-graded coins typically command higher prices in the market compared to ungraded coins. The assurance of authenticity and accurate grading instills confidence in buyers, leading to increased demand and higher premiums.
* **Enhanced Liquidity:** PCGS-graded coins are easier to sell due to their recognized and trusted grading. The standardization of grading simplifies the buying and selling process, making it easier to find buyers and negotiate fair prices.
* **Protection from Fraud:** PCGS’s authentication process protects collectors from purchasing counterfeit or altered coins. This reduces the risk of financial loss and ensures that collectors are acquiring genuine numismatic items.
* **Preservation of Condition:** The encapsulation process protects coins from environmental damage and handling, preserving their condition and value over time. This is particularly important for rare and valuable coins.
* **Market Transparency:** PCGS’s population reports provide valuable insights into the rarity and scarcity of specific coins, helping collectors make informed investment decisions. This data-driven approach enhances market transparency and reduces the risk of overpaying for common coins.
* **Peace of Mind:** Knowing that a coin has been authenticated and graded by a reputable service like PCGS provides peace of mind to collectors and investors. This confidence allows them to focus on enjoying their hobby and building their collections.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of PCGS
PCGS has established itself as a gold standard in coin grading, earning the trust of collectors and investors worldwide. However, it’s essential to provide a balanced perspective, acknowledging both its strengths and limitations.
From a user experience standpoint, submitting coins to PCGS is a straightforward process. The online submission form is user-friendly, and the instructions are clear. The turnaround time for grading can vary depending on the service level selected, but PCGS generally meets its stated deadlines.
PCGS’s grading accuracy is generally considered to be very high, although subjective elements are involved in grading. There can be slight variations in grading between different graders, but PCGS strives to maintain consistency and fairness.
**Pros:**
1. **Unmatched Reputation:** PCGS is the most recognized and respected coin grading service in the world, lending credibility to graded coins.
2. **Strong Guarantee:** PCGS’s grading guarantee provides financial protection to collectors in case of overgrading.
3. **Secure Encapsulation:** The tamper-evident holders protect coins from damage and tampering.
4. **Comprehensive Population Reports:** The population reports offer valuable insights into coin rarity and scarcity.
5. **Wide Acceptance:** PCGS-graded coins are widely accepted by dealers and collectors worldwide.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Cost:** PCGS grading fees can be relatively high, especially for lower-value coins.
2. **Subjectivity:** Grading is inherently subjective, and there can be slight variations in grading between different graders.
3. **Turnaround Time:** The turnaround time for grading can sometimes be lengthy, especially during peak periods.
4. **Perceived Overgrading:** Some critics argue that PCGS occasionally overgrades coins to inflate their value.
**Ideal User Profile:**
PCGS is best suited for serious collectors and investors who are looking to authenticate, grade, and protect their valuable coins. It is particularly beneficial for those buying or selling coins in the higher price ranges.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **NGC (Numismatic Guaranty Corporation):** NGC is another leading coin grading service with a strong reputation for accuracy and integrity.
* **ANACS (American Numismatic Association Certification Service):** ANACS is the oldest coin grading service in the United States and offers a more affordable option for grading lower-value coins.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:**
PCGS remains the gold standard in coin grading, offering unparalleled expertise, security, and market recognition. While the cost can be a barrier for some, the benefits of using PCGS far outweigh the drawbacks for serious collectors and investors. We highly recommend using PCGS for grading valuable coins to maximize their value and protect your investment.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about bicentennial quarter errors:
**Q1: What is the most valuable bicentennial quarter error?**
A1: The most valuable bicentennial quarter errors are typically those with dramatic errors, such as off-center strikes, double strikes, or significant die errors, combined with a high grade. The exact value varies based on market demand and condition.
**Q2: How can I tell if my bicentennial quarter is a proof coin?**
A2: Proof coins have a mirror-like surface and sharp details. They were specially struck for collectors and are typically found in pristine condition. Look for a deep, reflective shine and well-defined features.
**Q3: What does “no mint mark” mean on a bicentennial quarter?**
A3: Bicentennial quarters without a mint mark were struck at the Philadelphia Mint. Coins with a “D” mint mark were struck at the Denver Mint, and those with an “S” mint mark were struck at the San Francisco Mint (primarily for proof coins).
**Q4: Are silver bicentennial quarters worth more than clad quarters?**
A4: Yes, silver bicentennial quarters (struck in 40% silver) are worth significantly more than clad (copper-nickel) quarters. These were specially produced for collectors and are easily identifiable by their silver color.
**Q5: How do I protect my bicentennial quarter error from damage?**
A5: The best way to protect your coin is to encapsulate it in a coin holder or submit it to a grading service like PCGS or NGC. Avoid handling the coin directly, as oils from your skin can damage the surface.
**Q6: What is a die crack and how does it affect the value of a bicentennial quarter?**
A6: A die crack is a fracture in the die that appears as a raised line on the coin. The value of a coin with a die crack depends on the severity and location of the crack. More prominent and visually appealing die cracks generally command a higher premium.
**Q7: Where is the best place to sell my bicentennial quarter error?**
A7: You can sell your coin through online auction sites, coin dealers, or numismatic auctions. Choose a platform that caters to serious collectors and offers secure payment options.
**Q8: How can I learn more about coin collecting and numismatics?**
A8: The American Numismatic Association (ANA) offers educational resources, courses, and membership benefits for coin collectors. Local coin clubs are also a great way to connect with other collectors and learn from their experience.
**Q9: What is the difference between a doubled die and a double strike?**
A9: A doubled die is an error on the die itself, which is then replicated on multiple coins struck with that die. A double strike occurs when the coin is struck more than once during the minting process.
**Q10: Are there any specific bicentennial quarter errors that are currently trending in the collector market?**
A10: Certain dramatic errors, like significant off-center strikes or prominent doubled dies, often experience increased demand due to online exposure and collector interest. Stay updated on current trends through numismatic publications and online forums.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Value of Bicentennial Quarter Errors
Bicentennial quarter errors offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricacies of the minting process and the potential for finding valuable anomalies. By understanding the different types of errors, their causes, and the factors that influence their value, you can embark on a rewarding journey of coin collecting. Remember to consult with experts, utilize reputable grading services, and stay informed about market trends to maximize your collecting potential. Whether you’re a seasoned numismatist or a curious beginner, the world of bicentennial quarter errors holds endless possibilities for discovery and appreciation. Share your experiences with bicentennial quarter errors in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to coin grading for further insights.
